Power electronics: fueling the
development of electric vehicles
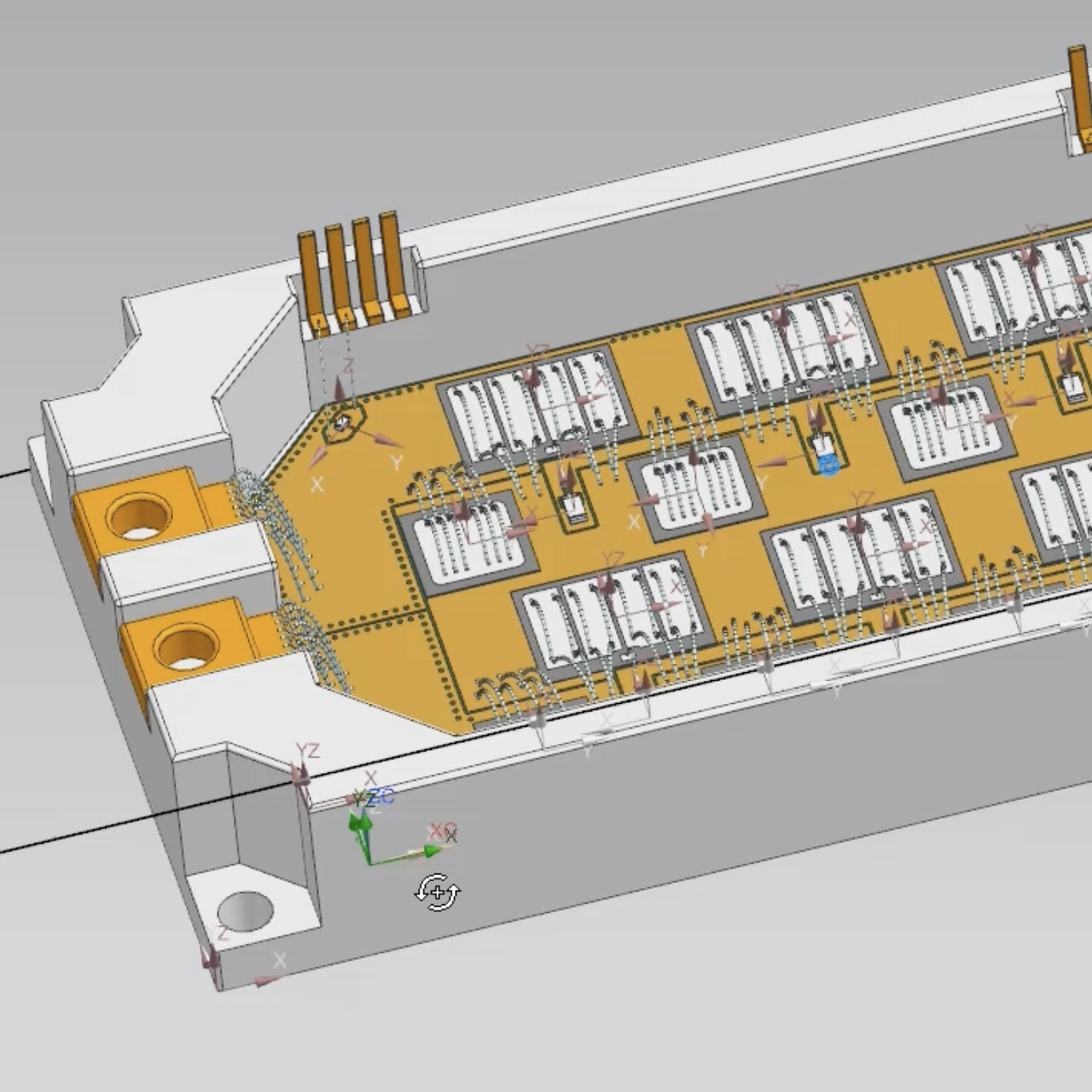
At the heart of power electronics are power modules, and a well-designed and efficient power module impacts most major systems within an electric vehicle (EV), like battery size or weight, cooling, vehicle range, and cost. As a result, each EV model requires a semi-custom design approach to power modules.